Hubble Nebula

Monoceros is a constellation of the equatorial region of the sky, representing the mythical single-horned beast, the unicorn. It is overshadowed by the brilliance of neighboring Orion but nevertheless contains several interesting deep-sky objects for amateur telescopes.
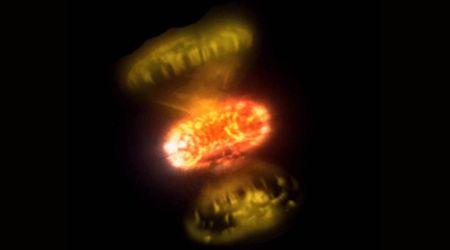
One of these deep sky showpieces is NGC 2261, more commonly known as “Hubble’s Variable Nebula”. Discovered by Sir William Herschel in 1783 and named for Edwin Hubble, NGC 2261 is a fascinating reflection nebula associated with the variable star R Monocerotis.
R is usually lost in the high surface brightness of the structure of the nebula, yet the whole thing varies in brightness by as much as two magnitudes with no predictable timetable – perhaps due to dark masses shadowing the star.
Although you can spot NGC 2261 through a 3-inch telescope, you will need at least a 10-inch scope at 200X to give this object some contrast. The nebula appears triangular, almost comet-like, with the comet’s “head” pointing southward. NGC 2261’s brightness appears even across its face and, except for the northern side, all edges are sharp.
Good views of this object can be obtained even from the suburbs, but in true darkness, you will discern noticeably more of the inner delicate features for which NGC 2261 has become so famous.
R Monocerotis and the nebula surrounding it are thought to be only a few hundred thousand years old. They may be a member of the open star cluster NGC 2264, but this is not certain. According to the California Institute of Technology, Hubble’s Variable Nebula was the first object photographed by the 200-inch Hale Telescope at Palomar Observatory. Hubble himself recorded an image of it on January 26, 1949.